Holographic sights are an exciting advancement in shooting technology. They provide a unique form of aiming that combines the benefits of both iron sights and red dot scopes.
The sight utilizes a special laser to project a holographic image of a reticle onto the surface of the lens. This reticle is visible in any light conditions, and it has proven to be an effective aiming tool.

But how do holographic sights work? We’ll, you’re about to find out.
This article is focused on portraying the working principle of holographic sights so that you can take good care of your sight and get the best out of it.
Without any further ado, let’s jump right in!
What Are Holographic Sights: Basic Introduction
Holographic sights are a type of optical device, sometimes referred to as “Holographic Weapon Sights (HWS)” or “Reflex Sights,” that project holograms on the lens in order to provide an enhanced aiming experience.
The most popular form of this technology utilizes a laser beam that bounces off of special reflective material, creating a visible reticle in the sight’s field of view.
This type of optics usually use a crosshair or other type of pattern for the reticle, and can be adjusted to different sizes and settings. The combination of red dots and holographic sights
provide an accurate, two-dimensional aiming solution for firearms.
Holographic sights are quite popular among shooters because they enable the shooter to create and lock in on the target without positioning the head in sight.
It does not lose its line even if the target moves left or right. Therefore, you do not need to set the target again if you move somewhat in any of the directions.
How Do Holographic Sights Work: Working Principle
The holographic sight uses a laser-transmission hologram based on non-magnifying gunsight that allows the user to watch through the glass window.
Using a laser diode, It creates a visible red laser in the reticle mode and then mount it on the prism.
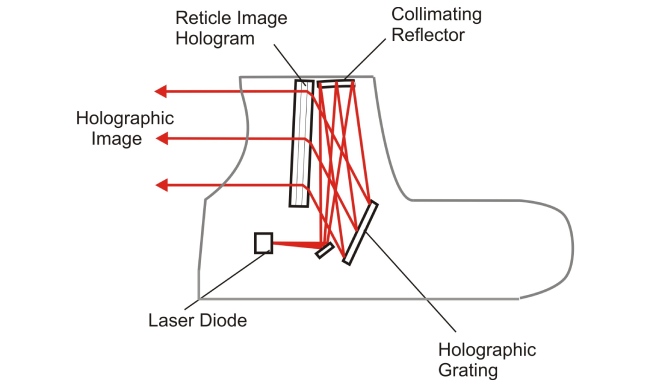
While aiming through the sight, the reticle will appear in the user’s field of view (FOV) and is superimposed on the point of aim.
The key benefit of holographic sights is that it does not lose their concentration even the shooter’s point of view changes slightly.
How Does A Holographic Sight Work: Understanding the Fundamentals
Now is the time to take on some fundamental properties of holographic sights.
Reticles
As mentioned above, the reticles in a holographic sight are created using a laser diode that is mounted on the prism.
The laser light then bounces off of reflective material to create an illuminated reticle image/pattern inside the sight’s viewfinder. This allows for quick and accurate aiming without having to adjust or re-position your head.
Battery Consumption
Additionally, the battery life of a holographic sight is impressive on it’s own. However, red dot sights are much more efficient that holographic sights when it comes to battery life.
Additionally, the battery life of a holographic sight is impressive on its own. However, red dot sights are much more efficient than holographic sights when it comes to battery power consumption.
This is because holographic sights require a higher-intensity laser, which means they consume more battery power. Typically, a holographic sight can last for up to thousands of hours, depending on the model, and the brightness level you’re using it in.
Focusing
Holographic sights also have the ability to auto-focus, further enhancing their accuracy. This is done through a process of aligning the prism with the reticle and then adjusting it until the image is clear.
This makes for an easier time aiming at longer distances, as it eliminates any need to make manual adjustments.
Night Vision
Like most other optics, holographic sights have night vision capabilities. This is done by utilizing a special infrared light that helps the user see in dark conditions.

The image will then appear with a greenish tint which makes it easier to utilize the sight in low-light environments.
Target Acquisition
Holographic sights are known for their quick target acquisition. This is because of the fact that they offer a wide field of view which makes it easier to spot and track targets.
The reticle pattern also allows the shooter to quickly lock on to their target while still providing precise aiming capability.
Field of View
The field of view is the area that you can see through your sight. Holographic sights typically have a wide field of view with some models offering up to 40 degrees or more.
This makes it easier to acquire targets quickly and efficiently since you don’t have to move your head around to see the target.
Magnification
Most holographic sights do not have magnification capabilities, as they are designed to be non-magnifying. This makes them ideal for close-range shooting and CQB situations.
That said, there are a few models that offer 1x magnification which can give you an extra edge when engaging at long distances. And you can also use a magnifier to increase the sight’s magnification capabilities if needed.
Here’s a video guide explaining the holographic technology for better understanding.
Holographic Sights – Pros & Cons
Pros of Holographic Sights
- Wide field of view
- Quick target acquisition
- Night vision capability
- Autofocus for accuracy
Cons of Holographic Sights
- Expensive compared to red dot sights
- Higher battery consumption than red dot sights
- No magnification capabilities on most models
And with that, we’ve reached the end of our today’s discussion. We tried to answer the question “how do holographic sights work” from some different technological point of view and hopefully, all these information will help you choose the perfect one for you.
Thanks for reading this far. Please feel free to share your thought and opinions on holographic sights and what worked the best for you in the comment section below. I wish you all a great weekend ahead, and happy shooting to you!
FAQs
What Is the Range of a Holographic Sight?
Generally speaking, most holographic sights have an effective range of up to 150 yards while some models may be able to reach even further. The maximum range of a holographic sight depends on the model and its specs.
Can You Magnify a Holographic Sight?
Some holographic sights do have a small amount of magnification, usually 1x. However, in most cases, you will need to use an external magnifier to increase the sight’s magnification capabilities.
Do Holographic Sights Affect Astigmatism?
No, holographic sights do not affect astigmatism. In fact, the wide field of view and autofocus capabilities make them easier to use for people with astigmatism.
Why Are Holo Sights So Expensive?
Holographic sights are more expensive than red dot sights due to their higher-end components and technology. They utilize more efficient laser images which adds to the cost. Additionally, the process of creating a hologram is much more complex than that of a standard reticle, so it requires precision manufacturing resulting in a steeper price tag.
Do Holographic Sights Have Parallax?
Yes. Despite what many people think, holographic sights do have parallax. However, most models are designed to minimize or reduce the effects of any parallax for improved accuracy.









Leave a Comment